Differential pressure is the pressure difference between two independent measuring points. This parameter is essential for monitoring and controlling processes in various industrial and scientific applications.
Methods for Measuring Differential Pressure
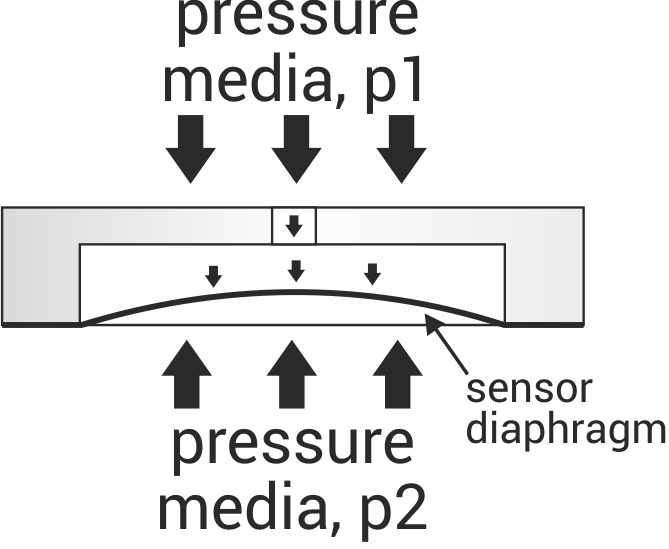
- Single Diaphragm Sensors:
True differential pressure can be measured with a single diaphragm sensor equipped with two independent pressure connection ports. Each side of the diaphragm is exposed to a different pressure medium, and the sensor directly measures the pressure difference between the two sides. - Dual Absolute Pressure Sensors:
Alternatively, differential pressure can be calculated by using two absolute pressure sensors. Each sensor measures pressure independently at separate points, and the difference is determined mathematically. This method is commonly used when existing absolute pressure measurements are available or when a direct differential pressure sensor is not practical.
Applications of Differential Pressure Measurement
- Filter Monitoring:
Differential pressure is often used to monitor the condition of filters in gas or air systems. As contamination builds up in a filter, the flow resistance increases, leading to a higher differential pressure. This measurement helps identify when a filter requires cleaning or replacement, ensuring system efficiency and preventing equipment damage. - Clean Room Control:
Differential pressure is a critical parameter in clean room environments, such as those used in semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. Maintaining a slightly elevated (positive) room pressure prevents contaminants from entering the controlled environment. Measuring and controlling differential pressure helps ensure the integrity of clean room conditions. - Flow Measurement:
Differential pressure can be used to determine the flow rate of gases or liquids in a system. By measuring the pressure drop across an obstruction or orifice in a flow path, the flow rate can be calculated based on established fluid dynamics principles. - HVAC Systems:
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, differential pressure measurements help optimize airflow, monitor duct systems, and ensure proper ventilation. - Safety Systems:
In applications such as pressure vessels or pipelines, differential pressure monitoring can detect blockages, leaks, or abnormal conditions, ensuring operational safety.
Key Benefits of Differential Pressure Measurement
- Enhances system performance by identifying inefficiencies or failures (e.g., clogged filters or restricted flow).
- Helps maintain controlled environments by ensuring pressure stability in critical applications.
- Provides valuable diagnostic data for predictive maintenance and troubleshooting.
By leveraging precise differential pressure measurements, industries can optimize their processes, reduce operational costs, and maintain stringent safety and quality standards.




