Absolute Pressure Measurement Explained
An absolute pressure measurement or pressure value exerted by a gas, vapor or liquid is a pressure value measured relative to a perfect reference vacuum. A perfect vacuum pressure is defined as zero pressure and consequently a fixed reference for measuring the absolute pressure.
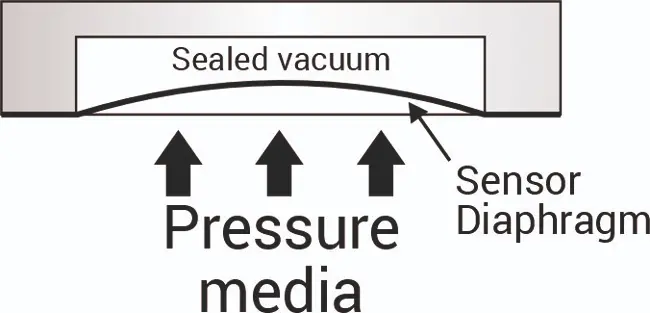
Absolute pressure can be measured using an electronic diaphragm sensor, where the measured pressure is applied on one side of the diaphragm, while the other side of the diaphragm is exposed to a permanently sealed vacuum.
Absolute pressure applications
One application for absolute pressure sensors is measuring barometric pressure variations due to changes in high and low atmospheric pressure created by weather patterns.
Another example is determining altitude by measuring change of ambient pressure as function of elevation. However, compensation for changes in barometric sea-level pressure is required for accurate altitude measurement.




