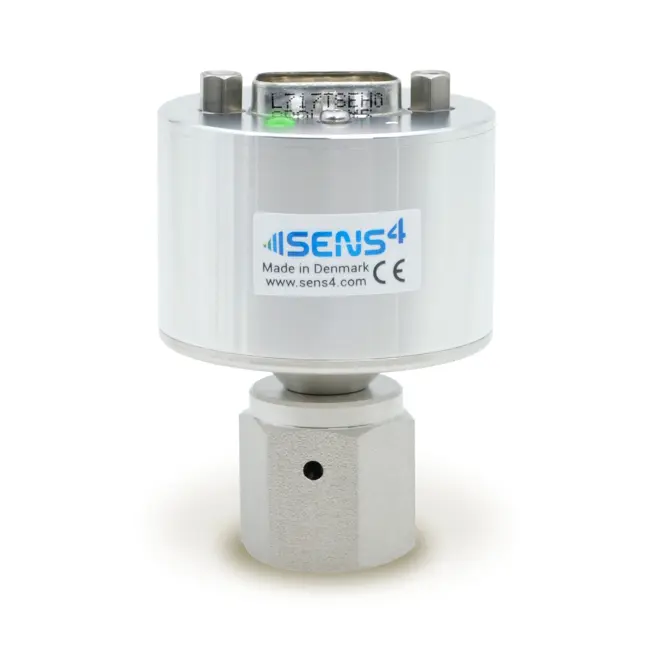
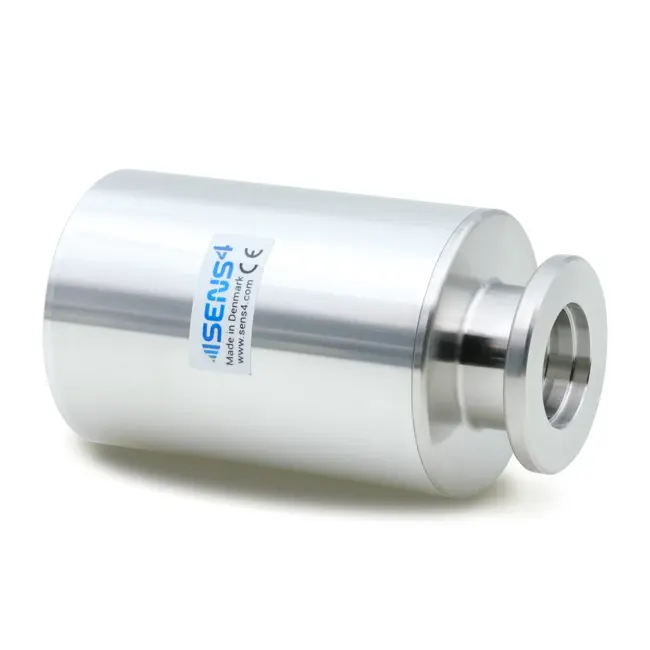
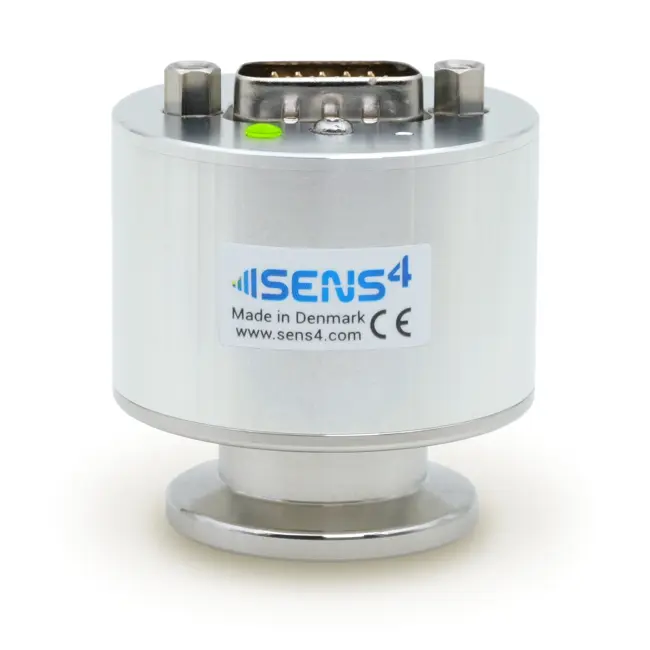
WHAT IS A HEAT-LOSS VACUUM GAUGE?
A heat-loss vacuum gauge or sensor is a device for measuring vacuum gas pressure by measurement of the pressure dependent thermal conductivity from a heated filament. The heat-loss gauge was first described by Marcello S. Pirani in 1906 and is commonly referred to as the Pirani gauge.
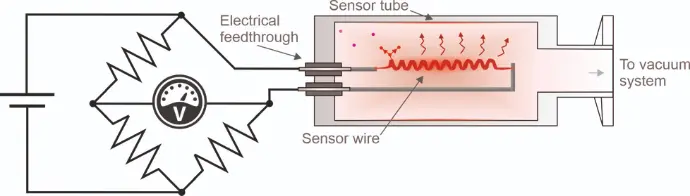
The heat-loss sensor can be made of a thin suspended wire surrounded by the vacuum gas pressure to measure. Improved performance of the heat-loss gauge has been achieved by use of MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) sensor design, where the resistive sensor filament is deposited on a suspended fixed diaphragm surrounded by the vacuum gas pressure to measure.
The heat-loss vacuum gauge has the advantage of covering a wide dynamic measurement range. The recently developed SmartPirani™ technology from Sens4 established in 2019 sets new performance standards for the heat-loss Pirani gauge by extending the measurement range of the SmartPirani™ heat-loss transducer down to 1.0E-6 mbar.




